If your customer's unhappy, everyone's unhappy!
Every great piece of software starts with a customer's big idea. It's your job as a professional software developer to bring that idea to life. But taking a vague idea and turning it into working code - code that satisfies your customer - isn't so easy. In this chapter you'll learn how to avoid being a software development casualty by delivering software that is needed, on time, and on budget. Grab your laptop, and let's set out on the map to shipping great software.
Most projects have two major concerns :
Talk to most customers, besides their big idea, they've probably got two basic concerns :
- How much will it cost?
- How long will it take?
The Big-Bang approach to development :
Big Bang : Work a log, and then, BANG, something huge and complex comes out of the work all at once... also known as "Going Dark" as the customer sees you at the beginning of the project, and then you disappear until software is delivered at the end.
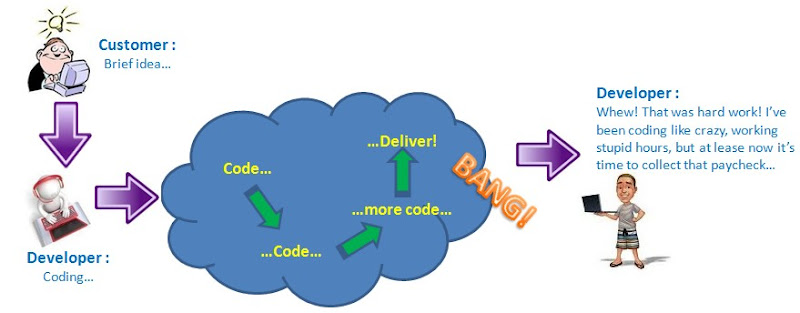
the Big-Bang ends with a Big Mess :
Even though a lot of work went into the project, your customer still could not satisfy with your output. If your customer isn't happy, you built the wrong software as well. Big bang software usually means working a whole lot, but it is also means not showing the customer much until your work is done. The risk with that approach is you think you're building what the customer wants with no real feedback until you think you're finished.
And, no matter how great YOU think your software is, it's the customer you have to make happy. So if the customer doesn't like what you've built, don't waste time trying to tell them they're wrong. Just get ready to do some rework.
But how do you figure out what the customer really wants? It's not always easy...
- Great software development is...
We've talked about several things that you'll need for successful software.
You have got the customer's big ideas to deal with, their money you're spending, and a schedule you've got to worry about. You've got to get all of those things right if you're going to build consistently great software :

Getting to the goal with ITERATION :
The secret to great software development is iteration. You've already seen that you can't simply ignore the customer during development. But iteration provides you a way to actually ask the question, at each step of development, "How am I doing?"
Here are two projects : one without iteration, and one with :
- Without iteration...
- With iteration...

- An iteration produces working software
With iteration, you check every step of the way that you're going in the right direction. That means making sure your software builds from almost the same as your customer want. 20 days is suggested to be an iteration according to experience. But you had better not to have long period where code doesn't work or compile, even if it's just small bits of functionality.
Then you show your customer those little pieces of functionality. It's not much, sometimes, but you can still get a OK from the customer.
Think about how most software is developed: You gather requirements (what your customer wants), build a design for the entire project, code for a long time, and then test everything. It looks a bit like this :

- Each iteration is QUALITY software
But suppose you didn't look at iteration as just a way to write big software. Think of iteration as little cycles, where you're gathering requirements, designing, writing code, and testing. Each cycle produces working, quality software :

- Your iteration length should be at the right tempo for YOUR project
An iteration helps you stay on track, and so you might decide to have iterations that are shorter or longer than 20 days. Twenty days might seem like a long time, but factor in weekends, and that means you're probably going to get 20 days of actual productive work iteration as a good starting point within a month, and then you can tweak for your project as needed.
The key here is to iterate often enough to catch yourself when you're deviating from the goal, but not so often that you're spending all your time preparing for the end of an iteration. It takes time to show the customer what you've done and then make course corrections, so make sure to factor this work in when you are deciding how long your iterations should be.
Iteration handles change automatically :
Your iteration plan is already structured around short cycles, and is built to handle lots of individual features. Here's what you need to do while encounter new features being plugged in unexpectedly :
1. Estimate the new features
2. Have your customer prioritize the new features
3. Rework your iteration plan
4. Check your project deadline
- Iteration is more than a process
Regardless of the actual steps involved in the process you choose, iteration is a best practice. It's an approach that can be applied to any process, and it gives you a better chance of delivering what is needed, on time and on budget. Whatever process you end up using, iteration should be a major part.
Your software isn't complete until it's been RELEASED :
You added the new features, and now you and your team have finished the project on time and on schedule. At every step of the way, you've been getting feedback from the customer at the end of each iteration, incorporating that feedback, and new features, into the next iteration. Now you can deliver your software, and then you get paid!

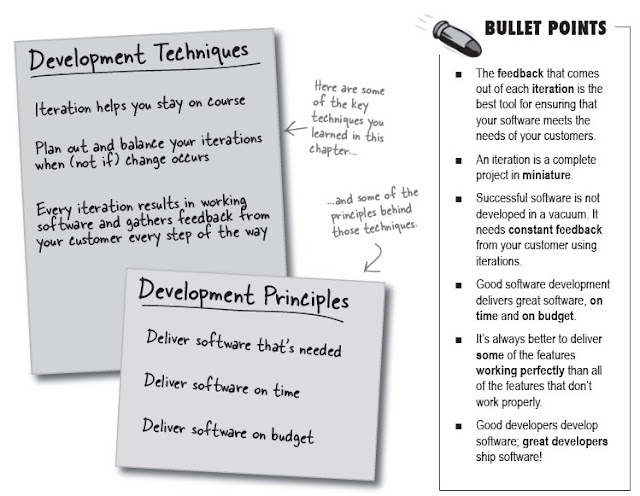
Software Development is all about developing and delivering great software. In this chapter, you learned about several techniques to keep you on track. Below is the tool-tips for you to review :



沒有留言:
張貼留言