What is Priority and Why Should I Care?
When talking about processes priority is all about managing processor time. The Processor or CPU is like a human juggling multiple tasks at the same time. Sometimes we can have enough room to take on multiple projects. Sometimes we can only focus on one thing at a time. Other times something important pops up and we want to devote all of our energy into solving that problem while putting less important tasks on the back burner.
In Linux we can set guidelines for the CPU to follow when it is looking at all the tasks it has to do. These guidelines are called niceness or nice value. The Linux niceness scale goes from -20 to 19. The lower the number the more priority that task gets. If the niceness value is high number like 19 the task will be set to the lowest priority and the CPU will process it whenever it gets a chance. The default nice value is zero.
By using this scale we can allocate our CPU resources more appropriately. Lower priority programs that are not important can be set to a higher nice value, while high priority programs like daemons and services can be set to receive more of the CPU’s focus. You can even give a specific user a lower nice value for all of his/her processes so you can limit their ability to slow down the computer’s core services.
Checking the Priority of Running Processes
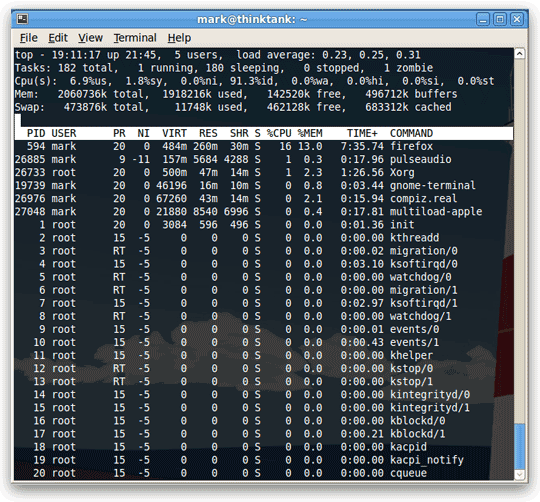
The easiest way to get a quick picture of what the current niceness priority on a process is to open up the top processes with:
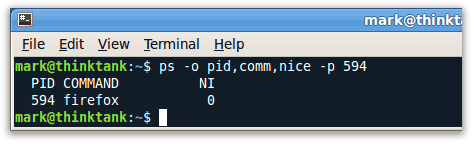
Another way you can get the nice value is use ps:
This will output the process ID, command, and nice value (marked as NI).
Setting priority on new processes
At this point you are probably wondering how you can set your own priority levels on processes. To change the priority when issuing a new command you do nice -n [nice value] [command]. e.g.:
This will increment the default nice value by a positive 10 for the command, ‘apt-get upgrade’ This is often useful for times when you want to upgrade apps but don’t want the extra process burden at the given time. Remember a positive number is gives less priority for a process.
Setting Priority on Existing Processes
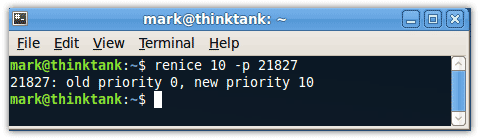
Obviously at some point you are going to want to alter the nice value of something that is already running. Just the other day I was doing an upgrade to Ubuntu Jaunty and Firefox started to become unusably slow. A quick renice command rescheduled the upgrade to a lower priority and I was back to surfing in no time. To change the priority of an existing process just do renice [nice value] -p [process id]:
This will increment the priority of the process with an id of 21827 to 10.
Note: Only root can apply negative nice values.
Setting Permanent Priority on all Processes for a Specific User
Sometimes it is helpful to give specific users lower priority than others to keep system resources allocated in the proper places like core services and other programs. You can set the default nice value of a particular user or group in the /etc/security/limits.conf file. It uses this syntax: [username] [hard|soft] priority [nice value]. e.g.:
- backupuser hard priority 1
* VBird - 第十六章、程序管理與 SELinux 初探
* 12 TOP Command Examples in Linux
* 使用 renice 指令更改 Unix/Linux 上面程式執行的優先權(Scheduling Priority)

沒有留言:
張貼留言